This report tracks national and regional progress in implementing the G20 reforms to global over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives markets reforms following the 2008 Global Financial Crisis.
Overall implementation across the 24 FSB member jurisdictions of the G20’s OTC derivatives reforms was already well advanced by 2021, but there continues to be only incremental annual progress in the remaining gaps in implementation.
-
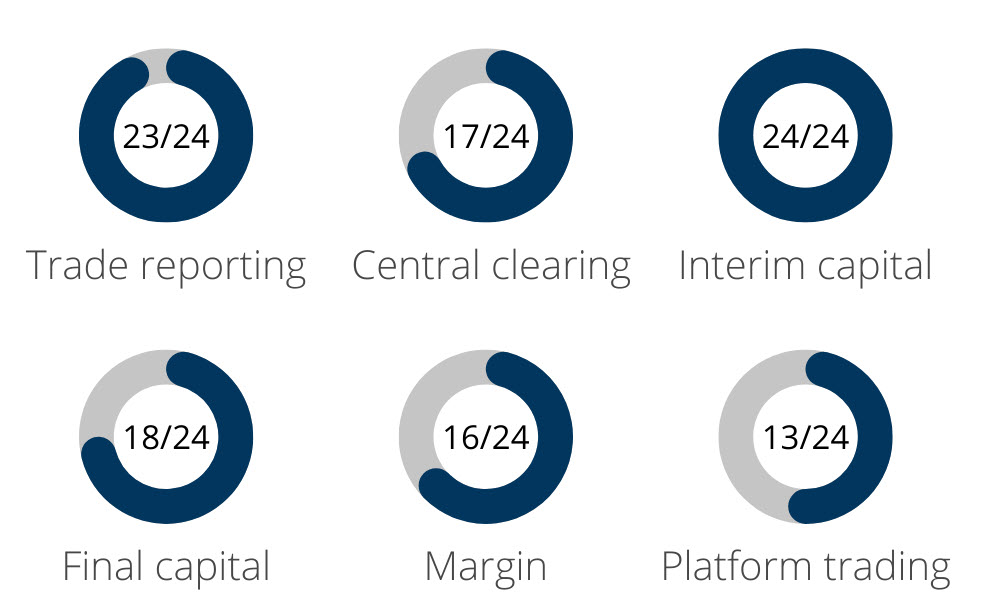
Capital requirements for non-centrally cleared derivatives (NCCDs): 18 FSB member jurisdictions have higher final capital requirements for NCCDs (up from 15 in 2021). Interim higher capital requirements for NCCDs are now in force in all FSB member jurisdictions.
-
Margin requirements for NCCDs: The number of jurisdictions where margin requirements are in force remains unchanged at 16. Two jurisdictions published final standards and three jurisdictions expect to implement the requirements in 2023.
-
Trade reporting: The number of FSB member jurisdictions where trade reporting requirements are in force remains unchanged at 23. In the remaining one jurisdiction, preparations for authorising a trade repository are ongoing. Some jurisdictions report they have further strengthened the functioning of trade repositories and the reporting requirements.
-
Central clearing: The number of FSB member jurisdictions that have in force central clearing requirements remains unchanged at 17. Some jurisdictions are taking steps toward implementation of mandatory central clearing, including authorisation of a central counterparty (CCP) in the jurisdiction.
-
Platform trading: The number of jurisdictions with platform trading requirements in force remains unchanged at 13.
The report also notes that by September 2021 most jurisdictions had already withdrawn or not extended measures previously introduced in response to COVID-19 to alleviate the operational burden for OTC derivatives market participants, or had embedded changes to limit and mitigate excessive procyclicality into permanent supervisory frameworks. Since then, a few further withdrawals of temporary measures have been reported, as well as one case of temporary new measures that have since expired.
Number of FSB jurisdictions that have fully implemented reforms (where legislation framework is in place and standards/requirements are in force for over 90% of transactions)