Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments sit at the heart of international trade and economic activity. However, for too long cross-border payments have faced four particular challenges: high costs, low speed, limited access and insufficient transparency. Faster, cheaper, more transparent and inclusive cross-border payments would have widespread benefits for supporting economic growth, international trade, global development and financial inclusion.
G20 cross-border payments roadmap
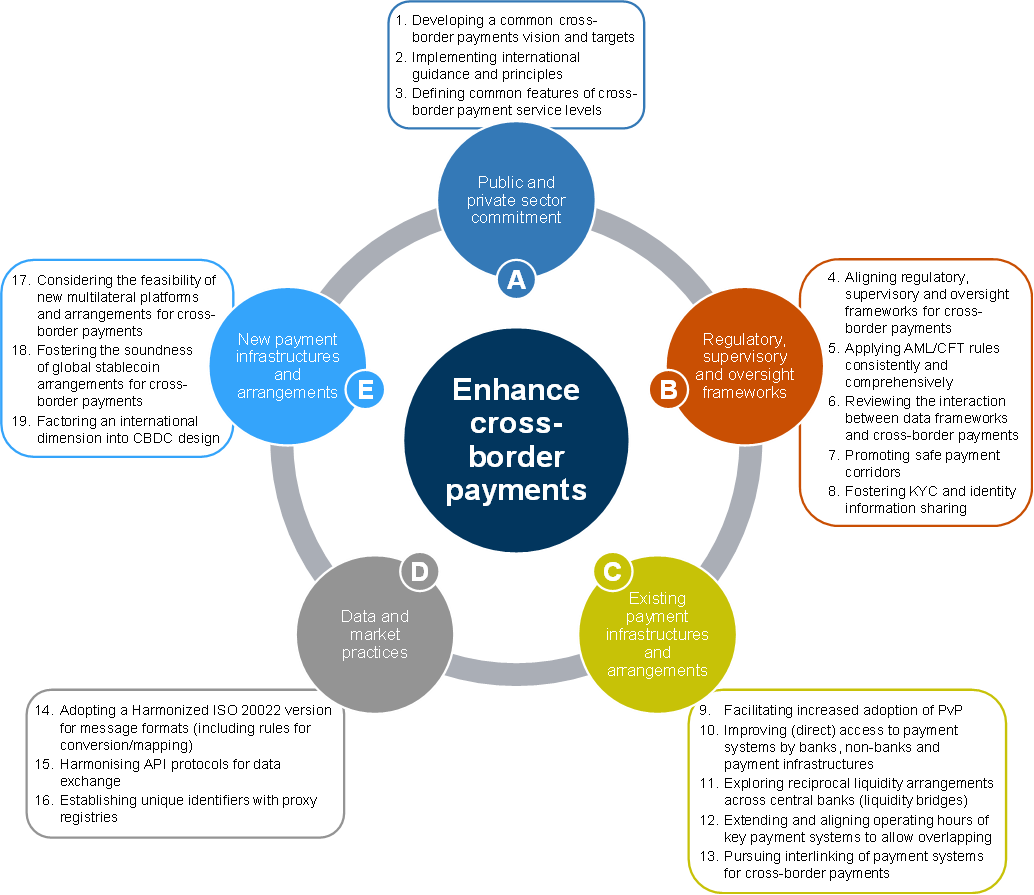
In 2020, at the request of the G20, the FSB, in coordination with the Bank for International Settlements’ Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI) and other relevant international organisations and standard-setting bodies, developed a roadmap to enhance cross-border payments (G20 Roadmap). Consisting of 19 building blocks, the G20 Roadmap provided a comprehensive, high-level plan for addressing the various frictions that underly the challenges of high costs, low speed, limited access and insufficient transparency in cross-border payments. It was designed to be flexible and to adapt over time as the work progresses and the cross-border payments landscape evolve, as well as to adjust to changing priorities and resourcing considerations as necessary.
Overview of the focus areas and associated building blocks
Over the subsequent two years, the FSB, CPMI and other partner organisaitons examined the full range of approaches and models to address the frictions underlying the challenges. Across the G20 Roadmap’s 19 building blocks, a wide range of issues, technologies and arrangements (current and future) were closely examined. The various workstreams developed analyses and recommendations in the form of best practices and updated guidance, and explored both improvements in existing arrangements and potential new multilateral platforms and arrangements. In addition, the FSB developed and the G20 endorsed a set of quantitative targets that define the Roadmap’s ambition and create accountability.
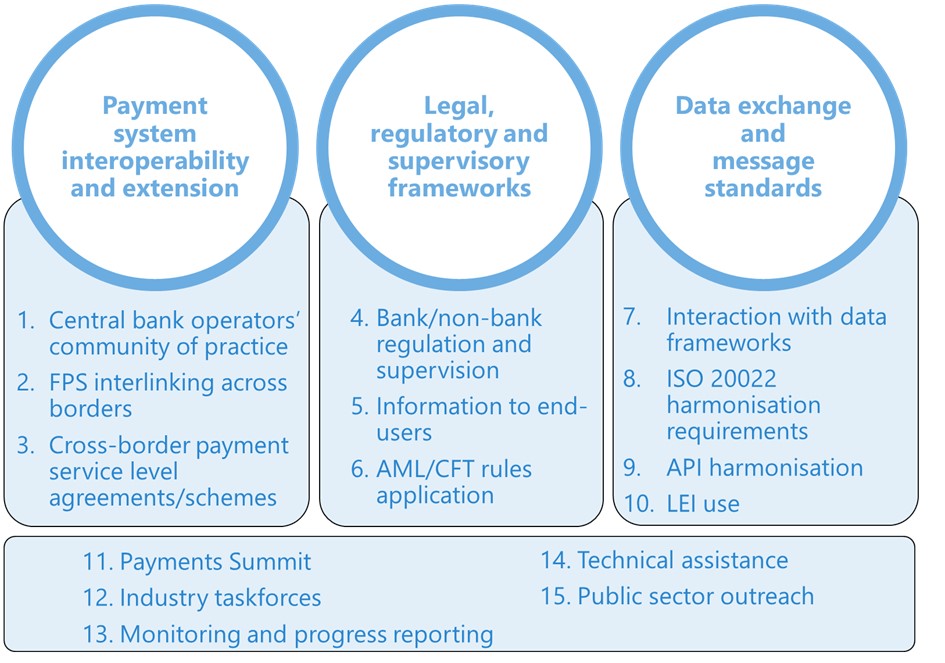
Based on the foundational work over the first two years of the Roadmap, the FSB, in October 2022, published a prioritisation plan and engagement model for taking the G20 Roadmap forward, followed, in February 2023, by the publication of a revised G20 Roadmap centered around 15 priority actions. The plan and priority actions reflect the Roadmap’s transition from analyses and stocktakes to the implementation of practical projects that will best help to achieve the targets that have been set for cross-border payments.
Cross-border Payments priorities
Progress monitoring
The FSB coordinates the implementation of the roadmap through its Cross-Border Payments Coordination Group (CPC) and reports on progress to the G20. The FSB has committed to providing two annual updates to the G20 and public, one on the progress made over the previous year in moving forward the priority actions and the other monitoring progress toward the G20 targets using key performance indicators.
Private-sector engagement at all levels
Extensive engagement with the private sector has been integral to the Roadmap since its inception. With the advent of the priority actions, engagement with the private-sector engagement was strengthened to ensure it was occurring at all of the necessary levels, from the technical to the strategic.
Read more here.
G20 targets for enhancing cross-border payments
In 2021, the G20 Leaders endorsed the Targets for Addressing the Four Challenges of Cross-Border Payments: Final Report (Targets report), which established 11 global targets across three market segments: wholesale payments, retail payments, and remittances. These targets define the Roadmap’s ambition for addressing the four challenges, create accountability and provide a common vision for the improvements sought under the Roadmap.
Read more here.
Correspondent banking and remittances
The FSB launched its four-point action plan in November 2015 to assess and address the decline in correspondent banking relationships. The plan covers:
-
Further examining the dimensions and implications of the issue;
-
Clarifying regulatory expectations, including guidance from FATF and BCBS;
-
Domestic capacity-building in jurisdictions that are home to affected respondent banks; and
-
Strengthening tools for due diligence in correspondent banks.
The FSB’s March 2018 recommendations to address problems that remittance service providers have accessing banking services cover:
-
Promoting dialogue and communication between the banking and remittance sectors;
-
International standards and oversight of the remittance sector;
-
The use of innovation in the remittance sector and its possible role in enabling RSPs greater access to banking services; and
-
Technical assistance on remittance-related topics.
The FSB has published regular updates to the G20 on the ongoing work to address these issues. The Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures provides regular data on correspondent banking so that the FSB can assess whether the agreed actions are being successful.
The FSB’s work in this area has now been integrated into the G20 cross-border payments roadmap.