The Financial Stability Risks of Decentralised Finance
Growth of Defi has potential wide ranging implications for traditional financial markets, and Defi inherits vulnerabilities of that system and may amplify them.
Within the crypto-asset ecosystem, so-called decentralised finance (DeFi) has emerged as a fast-growing segment. DeFi is an umbrella term commonly used to describe a variety of services in crypto-asset markets that aim to replicate some functions of the traditional financial system while seemingly disintermediating their provision and decentralising their governance.
To date DeFi is mainly self-referential, meaning its products and services interact with other DeFi products and services rather than with the traditional financial system and the real economy, but TradFi players are beginning to enter the market. In addition, DeFi has integral connections to centralised crypto-asset trading, lending and borrowing platforms, through which participants exchange crypto-assets for one another or for fiat currency, often using stablecoins.
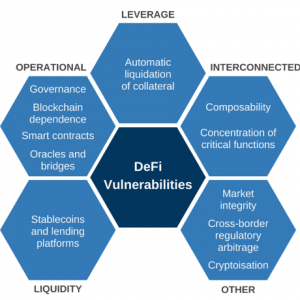
While the processes to provide services are in many cases novel, DeFi does not differ substantially from TradFi in the functions it performs. In attempting to replicate some of the functions of the traditional financial system, DeFi inherits and may amplify the vulnerabilities of that system. This includes well-known vulnerabilities such as operational fragilities, liquidity and maturity mismatches, leverage, and interconnectedness.
The extent to which these vulnerabilities can lead to financial stability concerns largely depends on the interlinkages and associated transmission channels between DeFi, TradFi and the real economy. These interlinkages have so far been limited, as shown by the modest impact of the May/June 2022 crypto-asset market turmoil and the November 2022 FTX collapse on TradFi. However, if the DeFi ecosystem were to grow significantly and become more mainstream, as a result of the broader adoption of crypto-assets and the development of real-world use cases, then interlinkages would deepen and the scope for spillovers to TradFi and the real economy would increase.
This report:
-
describes the DeFi ecosystem, its key elements and players, as well as the main products;
-
discusses financial vulnerabilities of DeFi, including those stemming from its specific features;
-
sketches possible scenarios for DeFi and the implications for financial stability; and
-
sets out additional work to analyse, monitor and address vulnerabilities in the DeFi ecosystem.